Laravel | Erstellen einer Starter-App
Inhaltsverzeichnis
TL;DR
Der Code für die in diesem Post erstelle Anwendung liegt hier.
Installation
Erstellen der Starter App
laravel new Laravel-Starter-App --jet --stack=livewire --api --teams --dark --pest --verification --database sqlite --git --quiet
Konfiguration der Datenbank
Die Konfiguration der Datenbank erfolgt in der bereits vorhandenen Datei .env.
Nach der Installation finden Sie dort die folgenden Einträge für eine MySQL Datenbankanbindung:
Datenbank SQLite verwenden
Bei Einrichten der Starter App wurde bereits SQLite vorselektiert:
DB_CONNECTION=sqlite
Leere Datenbankdatei erstellen
Die Starter App hat bereits eine leeren Datenbank im Ordner database mit dem Namen database.sqlite
Tabellen erstellen
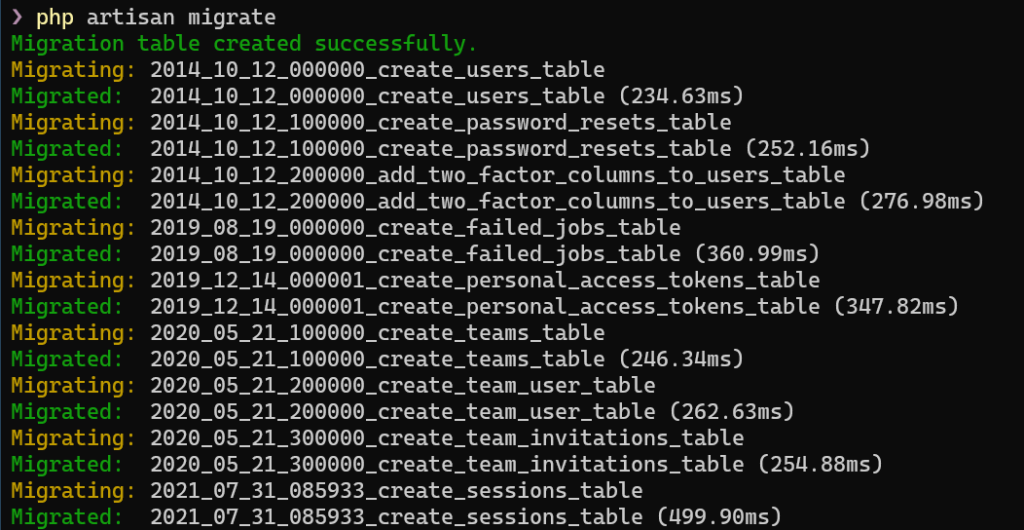
Die für Laravel notwendigen Tabellen wurden ebenfalls eingerichtet:
php artisan migrate
Hinweis: Die vorhandenen Tabellen können Sie sie über die Kommandozeile anzeigen:
sqlite3.exe .\database\database.sqlite ".tables"

Installation und Konfiguration des Frontend
Um mit dem Frontend arbeiten zu können, müssen zu ersten die notwendigen Komponenten installiert und das Frontend erstellt werden:
npm install npm run dev
Anzeigen der Anwendung
Die grundlegende Installation und Konfiguration ist abgeschlossen. Starten Sie die Anwendung durch das nachfolgende Kommando:
php artisan serve
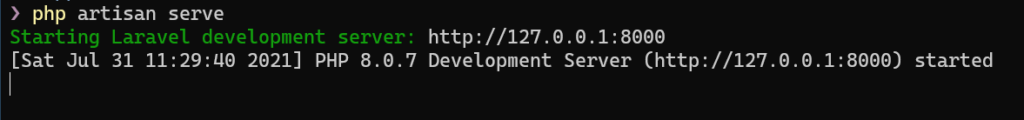
Öffnen Sie die Anwendung im Browser über den Link http://127.0.0.1:8000
Anmeldung und Authentifizierung
Die erstelle Laravel-Anwendung enthält bereits die Funktionalität, das sich Benutzer Registrieren und Anmelden können. Hierzu finden Sie auf der Startseite rechts oben entsprechende Links.

Mit den verwendeten Standardeinstellungen sin Ausreichend für das Einrichten neuen Benutzer.
Um eine höhere Sicherheit zu erreichen, werden diese Einstellungen so geändert, das einen Bestätigungsmail an den Benutzer gesendet wird. Erst durch den Klick auf den darin enthaltenen Bestätigungslink wird die Einrichtung des Benutzers abgeschlossen.
E-Mail Verification einrichten
Das Einrichten dieser E-Mail Verification erfolgt in mehreren Schritten.
Hinweis: Diese wurden ebenfalls durch die Starter App durchführt.
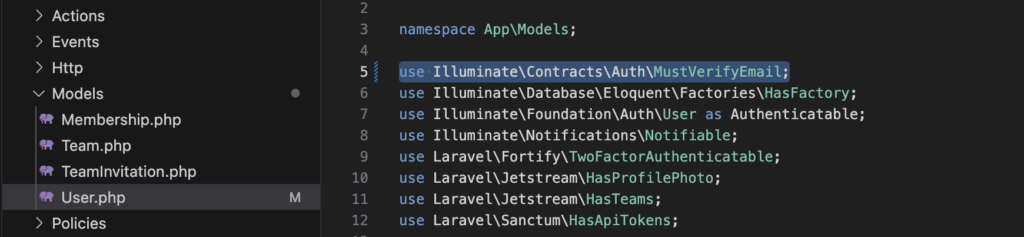
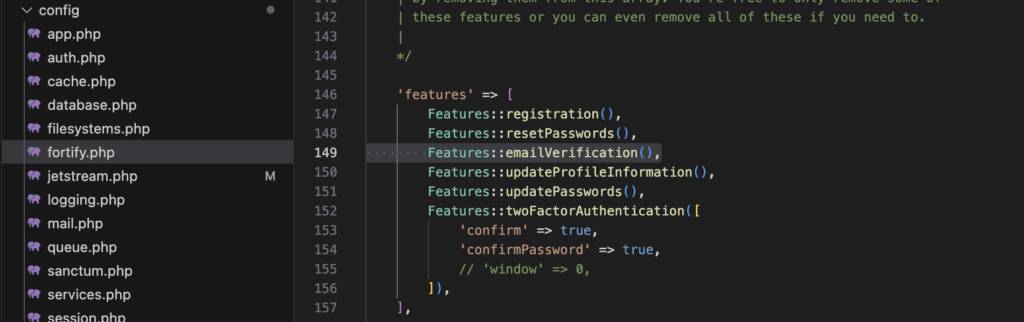
Aktivieren des Features emailVerification in der Datei config/fortify.php
Einrichtern der E-Mail-Verifizierung bei der Registrierung
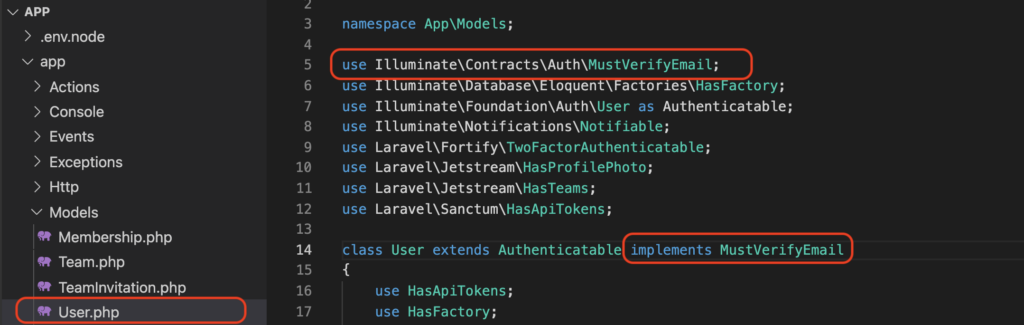
Passen sie die Datei app/User.php an:
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\MustVerifyEmail;
class User extends Authenticatable implements MustVerifyEmail
Festlegen der E-Mail Konfiguration
Damit Laravel eine E-Mail versenden kann wird der Zugang zu einem E-Mail Server verwendet. Hier benötigen wir die Zugangsdaten für den SMTP-Versand.
Für das Empfangen der Verifizierungsmail gibt es zwei Möglichkeiten:
- die Verifizierungsmail wird im Laravel-Log gespeichert
- die Verifizierungsmail wird an einen SMPT-Server gesenden
- sie können hier ihren eigenen SMTP-Server verwenden
- oder sie verwenden mailpit (Lokaler SMTP-Server für Tests)
Festgelegt werden diese Parameter wieder in der Datei .env:
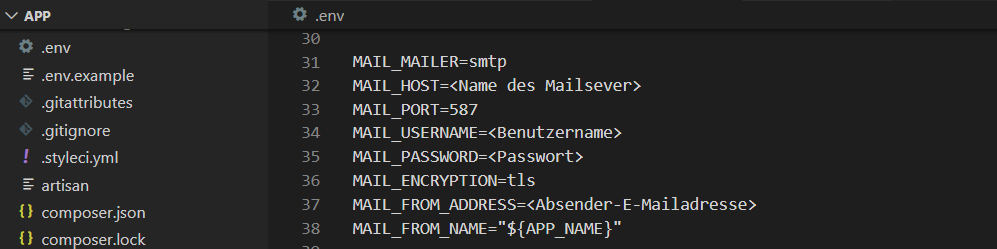
Die entsprechenden Werte hängen vom verwendeten Mailserver ab.
Laravel Log verwenden
Der Eintrag in der Datei .env lautet dann:
MAIL_MAILER=log
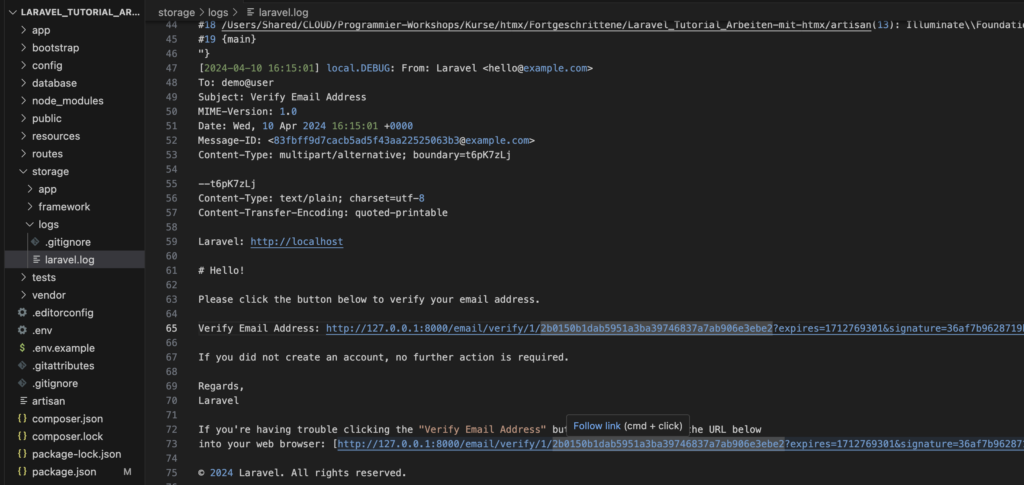
Die Verifizierungsmail finden sie dann in der Datei storage/logs/laravel.log:
Eigener SMTP-Server
Der Eintrag in der Datei .env lautet dann:
MAIL_MAILER=smtp
Zuerst müssen Sie bei ihrem Provider ein Mailkonto einrichten (Benutzer und Passwort). Testen Sie am besten diese Daten über den von ihrem Provider bereitgestellten Webmailer.
Die weiteren Werte (Port, Protokoll) entnehmen Sie der Dokumentation ihres Providers.
Nachfolgend zwei Beispiele:
| Provider | Strato | United Domains |
|---|---|---|
| MAIL_MAILER | smtp | smtp |
| MAIL_HOST | smtp.strato.de | smtps.udag.de |
| MAIL_PORT | 587 | 587 |
| MAIL_ENCRYPTION | tls | tls |
Lokaler SMTP-Server für Testzwecke: mailpit
Für Testzwecke können sie die E-Mail-Konfiguration auch vereinfachen, indem ein lokaler Mailserver verwendet wird: mailpit (https://mailpit.axllent.org/docs/install/)
Installieren sie diesen und starten sie ihn dann mit den Parametern aus der Laravel-Konfiguration: dem SMTP-Port aus der Datei .env. Passen sie zusätzlich den Parameter MAIL_MAILER an:
MAIL_MAILER=smtp
❯ mailpit -s 0.0.0.0:2525 INFO[2024/04/09 18:42:33] [smtpd] starting on 0.0.0.0:2525 (no encryption) INFO[2024/04/09 18:42:33] [http] starting on [::]:8025 INFO[2024/04/09 18:42:33] [http] accessible via http://localhost:8025/
mailpit Frontend öffnen
Klicken sie auf den angegeben Link der Ausgabe von mailpit, um das Frontend zu starten:
Benutzer einrichten
Starten Sie die Anwendung neu und richten Sie einen weiteren Benutzer ein
php artisan serve

Registrierung durchführen
Starten Sie die Registrierung über den Link Register auf der Startseite.

Geben Sie die notwendigen Benutzerdaten ein. Bestätigen Sie ebenfalls die Terms of Services, falls diese aktiviert sind. Wie sie diese aktivieren können sie hier nachlese.
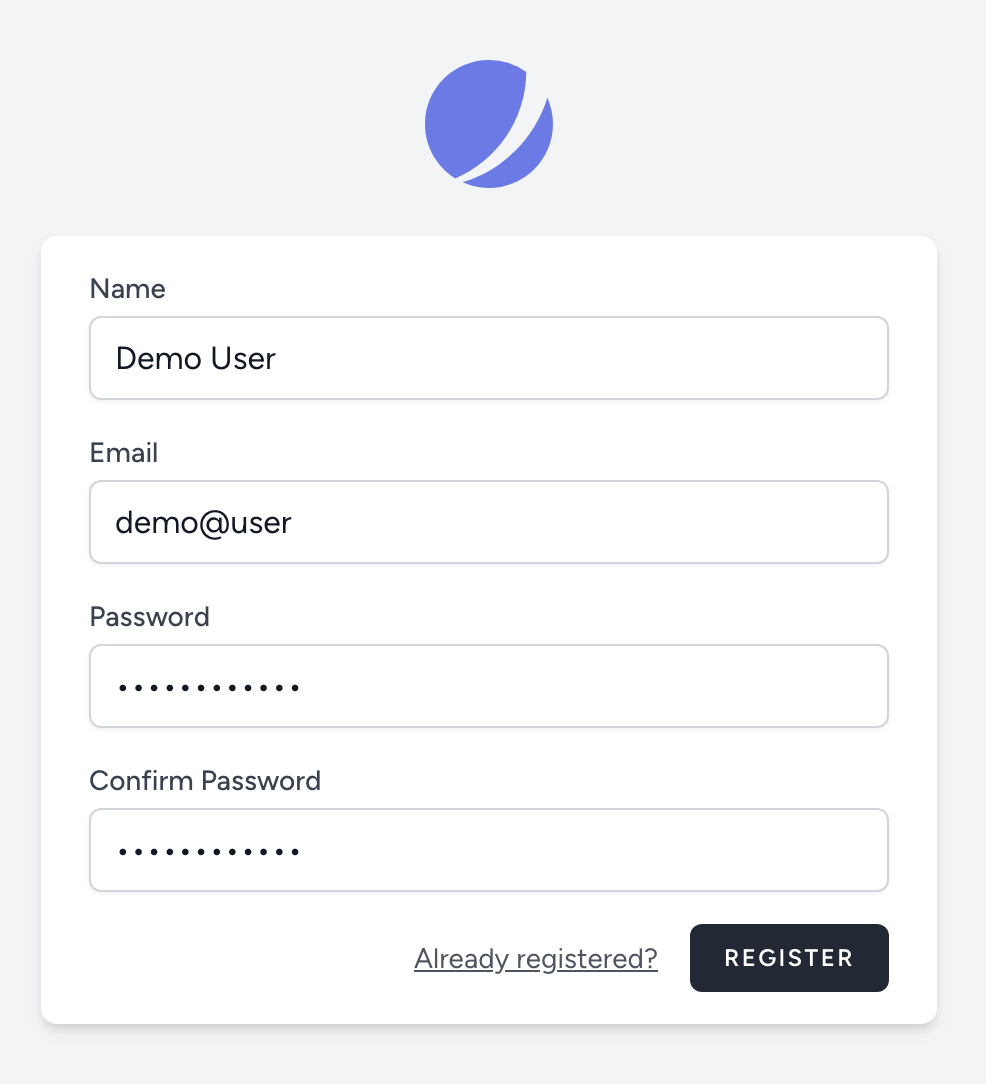
Bei erfolgreichen Versand der Bestätigungsmail erscheint diese Anzeige. Sie erhalten ebenfalls eine Bestätigungsmail an die verwendete E-Mail-Adresse.
Öffnen Sie die E-Mail und klicken Sie auf den Bestätigungslink. Achten Sie darauf, das der Link im gleichen Browser geöffnet wird, mit dem Sie die Registrierung durchgeführt haben.
Alternativ kopieren Sie einfach den Link, wechseln wieder zurück in das Registrierungsfenster und fügen den kopierten Link ein.
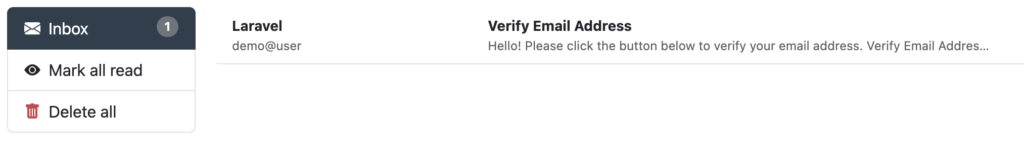
Wenn sie mit mailpit arbeiten, so sehen sie im Frontend, das eine neue E-Mail eingegangen ist:
Danach befinden Sie sich auf dem Dashboard der Anwendung. Die Registrierung hat somit funktioniert.
Mögliche Konfigurationsfehler
E-Mail Server ist falsch
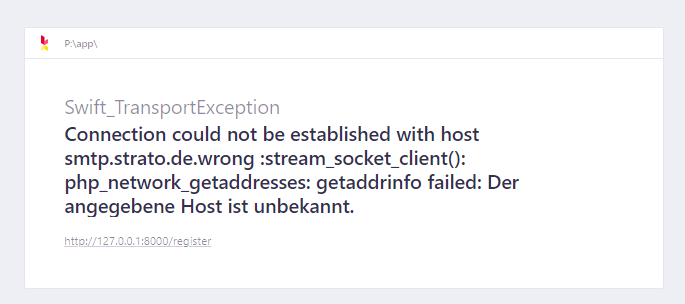
Fehlermeldung: Der angegebene Host ist unbekannt
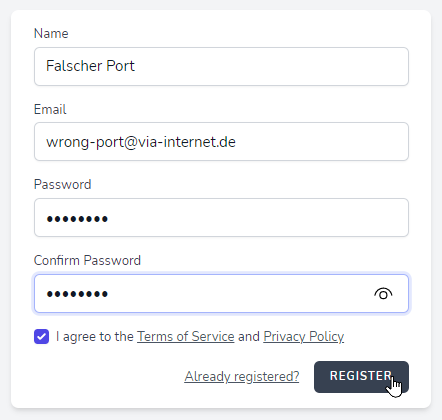
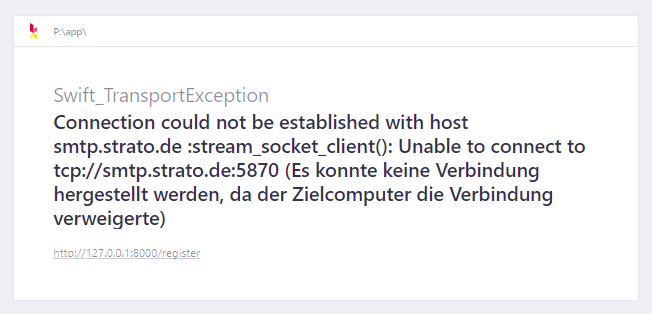
Port ist falsch
Fehlermeldung: Es konnte keine Verbindung hergestellt werden, da der Zielcomputer die Verbindung verweigerte
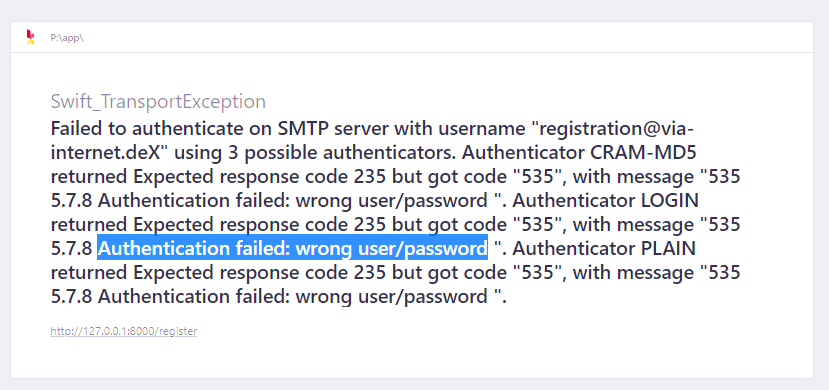
Benutzername oder Passwort sind falsch
Fehlermeldung: Authentication failed: wrong user/password
Weitere Anpassungen
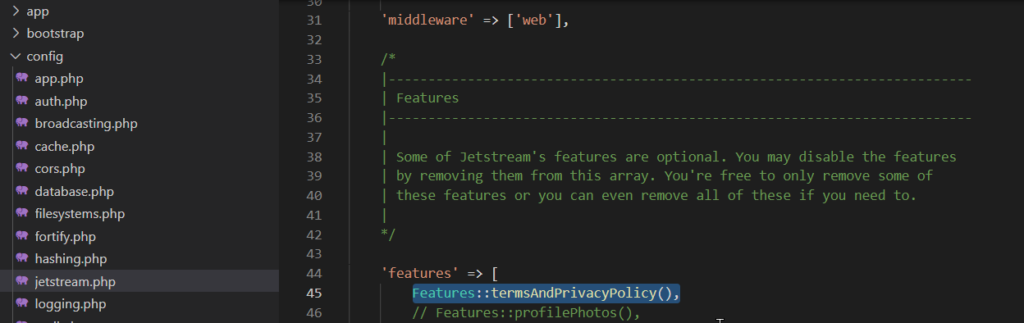
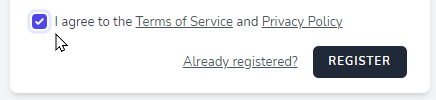
Terms of Services aktivieren
Aktivieren Sie dazu das Feature termsAndPrivacyPolicy in der Datei config/jetstream.php
Dadurch sehen sie im Registrierungsdialog ein zusätzliches Optionsfeld
Ändern der Sprache
Bearbeiten Sie in der Datei config/app.php die Einstellung locale. Ändern Sie den Wert auf 'de'.
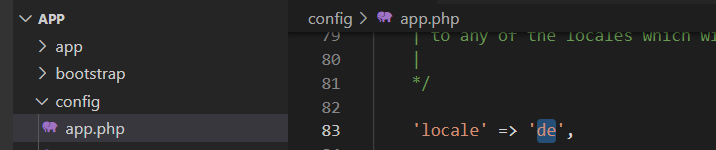
Nach einem Neustart der Anwendung werden aber weiterhin die englischen Texte angezeigt.
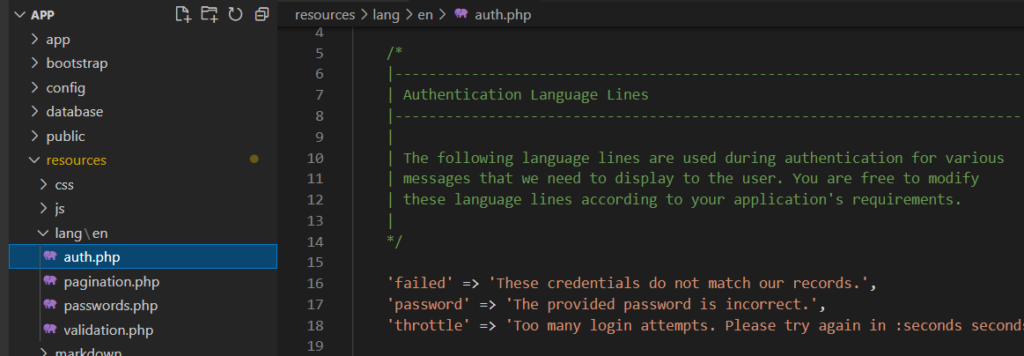
Die Ursache liegt an der nicht vorhandenen deutschen Übersetzung der verwendeten Texte. Prüfen Sie einfach den Ordner mit den vorhandenen Übersetzungen: resources/lang
Es gibt nur einen Unterordner en für die englischen Texte:
Zusätzlich zu den Übersetzungen muss noch ein weiterer Schritt erfolgen. Um ihre Anwendung komplett auf Mehrsprachlichkeit umzustellen dürfen keine Texte direkt angegeben werden.
Betrachten wir hierzu die Startseite, speziell die Links in der rechten oberen Ecke:
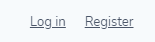
Der View für die Startseite wird in der Datei resources/views/welcome.blade.php definiert:
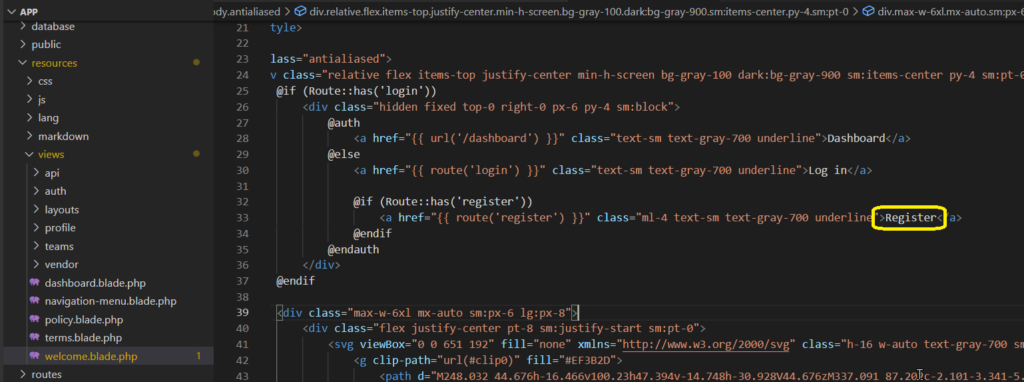
Wir sehen, das hier der Text direkt in englischer Sprache angegeben wird.
<a href="{{ route('register') }}" class="...">Register</a>Es ist sehr schwierig, eine automatische Übersetzung für alle Texte durchzuführen, wenn nicht angegeben wird, ob ein bestimmter Text übersetzt werden soll. Einfach alle Texte zu übersetzen kann zu Problemen führen.
Daher wird bei Laravel der Weg gewählt, explizit anzugeben, ob ein Text übersetzt werden soll.
Diese Angabe der nachfolgende Text soll übersetzt werden erfolgt mit Hilfe der Funktion __ (Der Name der Funktion lautet tatsächlich __, als zwei Unterstriche)
Anstatt
Register
schreiben wir nun
{{ __('Register') }}Dadurch erkennt Laravel (speziell die Blade Template Engine), das hier eine Übersetzung durchgeführt werden soll und sucht eine passenden Übersetzungstext.
Hier kommt nun der bereits angesprochen Ordner resources/lang ins Spiel. Erstellen Sie in diesem Ordner eine Datei de,json und verwenden Sie als Inhalt den nachfolgenden Text:
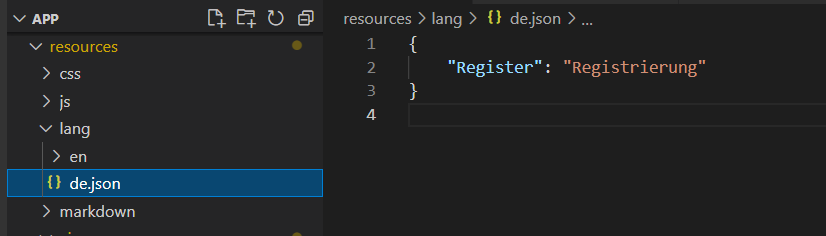
Nach einen Neustart der Anwendung sehen wir gewünschte Ergebnis:

Den gewünschten Übersetzungstext findet Blades anhand des angegebenen Textes innerhalb der Funktion __:
| welcome.blade.php | de.json |
|---|---|
 | 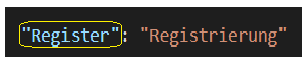 |
Die Übersetzung der Anwendung erfordert somit für alle Texte die gleichen Schritte
- Ermitteln des Views mit dem zu übersetzenden Text, z. B. Sample Text
- Einbinden des Textes in die Funktion , z. B.
{{ ('Sample text') }} - Hinzufügen der Übersetzung in der Datei
de.json, z. B."Sample text“: Beispieltext“
Erstellen einer neue Startseite
Die Startseite entspricht immer noch der Standardanwendung. Der entsprechende View ist welcome.blade.php.
Zur Startseite wird dieser View aber nicht durch den Namen, sondern durch eine Einstellung in der Datei routes/web.php
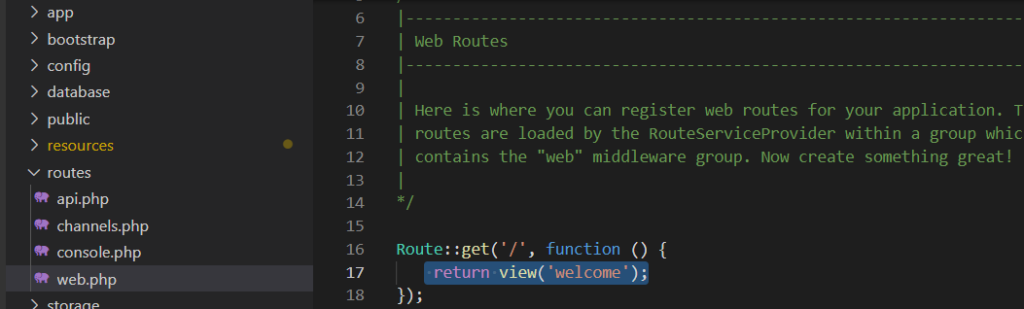
Mit Hilfe des von Laravel verwendeten Routing, wird festgelegt, welcher View angezeigt wird, wenn eine bestimmte URI aufgerufen wird.
In der vorhandenen Einstellung legt fest, das bei der Uri '/' der View 'welcome' angezeigt wird.
Einfache Startseite erstellen
Wir verwenden hier das in der Laravel Dokumentation beschrieben einfache Beispiel.
Erstellen Sie die Datei Datei resources/views/home.blade.php. Verwenden Sie als Inhalt den nachfolgenden Text
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello, {{ $name }}</h1>
</body>
</html>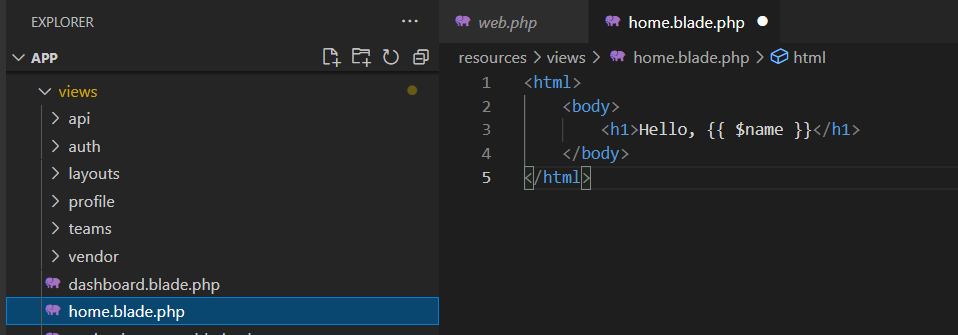
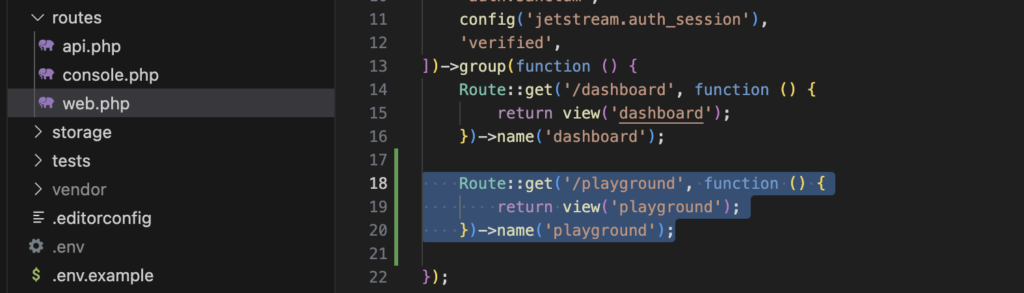
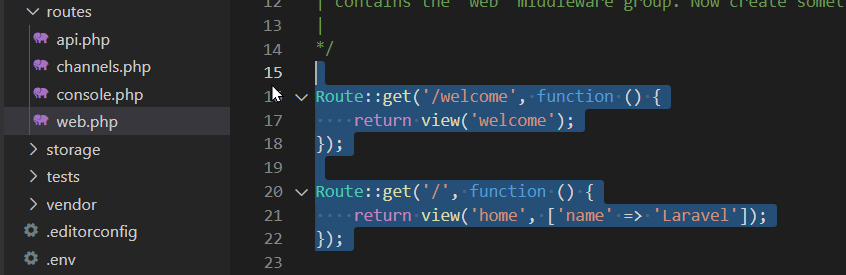
Routing anpassen
Passen Sie dann die Datei routes/web.php an.
Route::get('/welcome', function () {
return view('welcome');
})->name('welcome');
Route::get('/', function () {
return view('home', ['name' => 'Laravel']);
});Wir ändern die neue Startseite mit der Uri / und stellen die alte Startseite unter einer neuen Uri /welcome bereit.
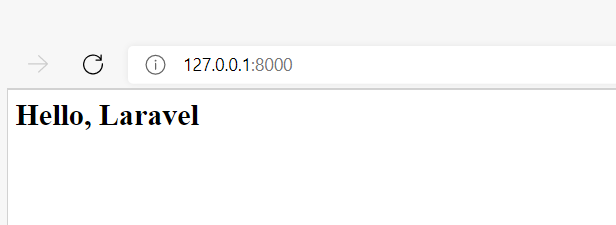
Neue Startseite anzeigen
Öffnen Sie nun wieder die Seite http://localhost:8000 oder aktualisieren Sie ein bereits geöffnetes Browserfenster:
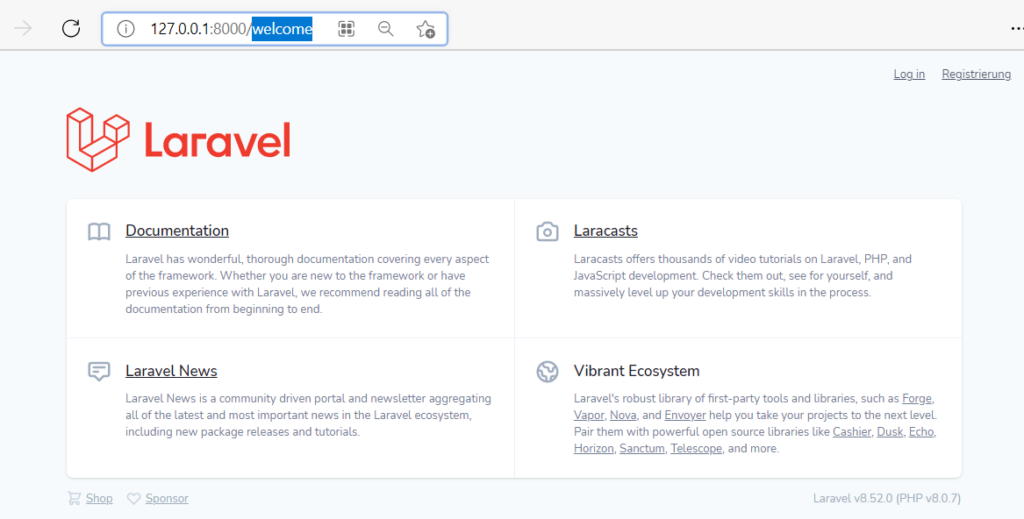
Die vorherige Startseite können wir über die Uri /welcome erreichen
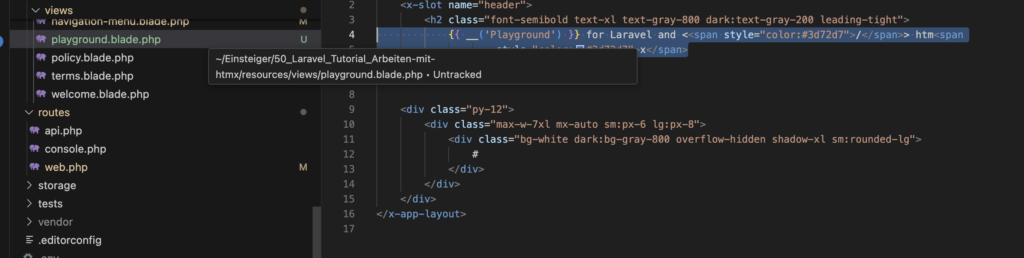
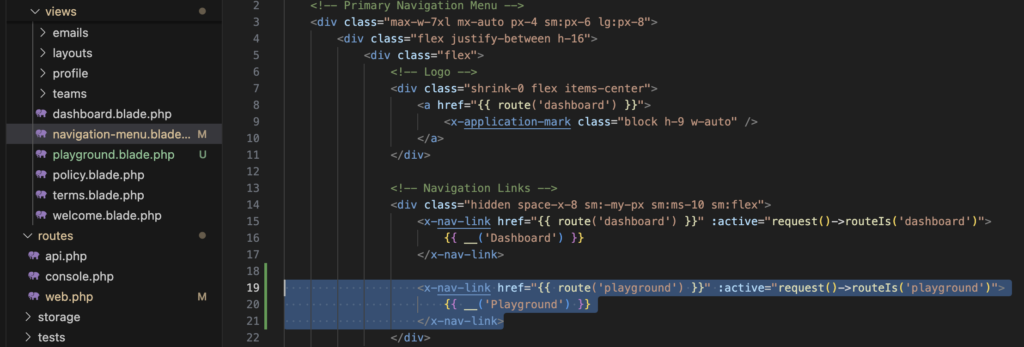
Erweitern Sie die Daten resources/views/navigation-menu.blade.php um einen Eintrag:
<!-- Navigation Links -->
<div class="hidden space-x-8 sm:-my-px sm:ml-10 sm:flex">
<x-jet-nav-link href="{{ route('dashboard') }}"
:active="request()->routeIs('dashboard')">
{{ __('Dashboard') }}
</x-jet-nav-link>
</div>
<div class="hidden space-x-8 sm:-my-px sm:ml-10 sm:flex">
<x-jet-nav-link href="{{ route('welcome') }}"
:active="request()->routeIs('welcome')">
{{ __('Welcome') }}
</x-jet-nav-link>
</div>Komponenten
Komponente erstellen
php artisan make:component MyComponent
Blade-Komponenten registrieren
You can register your jetstream blade components in App\Providers\JetstreamServiceProvider.php located in app\Providers folder.
Fügen sie die nachfolgende Funktion hinzu:
protected function registerComponent(string $component) {
\Illuminate\Support\Facades\Blade::component('jetstream::components.'.$component, 'jet-'.$component);
}Der nachfolgende Programmcode registriert ihre Komponente:
public function register() {
$this->registerComponent('subform');
}Sie können diese nun wie folgt nutzen:
<x-jet-subform>